New York taxes can be complex and challenging to navigate, especially for those unfamiliar with the state's tax system. Whether you're an individual taxpayer or a business owner, understanding how New York taxes work is crucial for ensuring compliance and optimizing your financial health. This guide aims to provide you with all the essential information you need to manage your tax obligations effectively.
Living in New York comes with its own set of financial responsibilities, and one of the most significant is taxation. The state imposes various types of taxes, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, and more. Each of these taxes plays a vital role in funding public services and infrastructure, but they also impact your disposable income and overall financial planning.
In this article, we will explore the intricacies of New York taxes, offering insights into how they are calculated, what exemptions may apply, and how you can minimize your tax burden legally. By the end, you'll have a clearer understanding of your obligations and be better equipped to make informed financial decisions.
Read also:Iraqi Dinar Revaluation Unlocking The Potential Of Iraqs Currency
Table of Contents
- Overview of New York Taxes
- New York State Income Tax
- Sales Tax in New York
- Property Taxes in New York
- Business Taxes in New York
- Estate and Inheritance Taxes
- Tax Exemptions and Credits
- Filing Your New York Tax Return
- Penalties for Non-Compliance
- Useful Resources for Taxpayers
Overview of New York Taxes
New York taxes are designed to support the state's infrastructure, public services, and education systems. These taxes are collected at various levels, including state, county, and local municipalities. Understanding the different types of taxes in New York is the first step toward effective tax planning.
Types of Taxes in New York
The primary categories of taxes in New York include:
- Income tax
- Sales tax
- Property tax
- Business taxes
- Estate and inheritance taxes
Each type of tax has its own set of rules, rates, and exemptions. It's important to familiarize yourself with these details to ensure compliance and take advantage of any available deductions or credits.
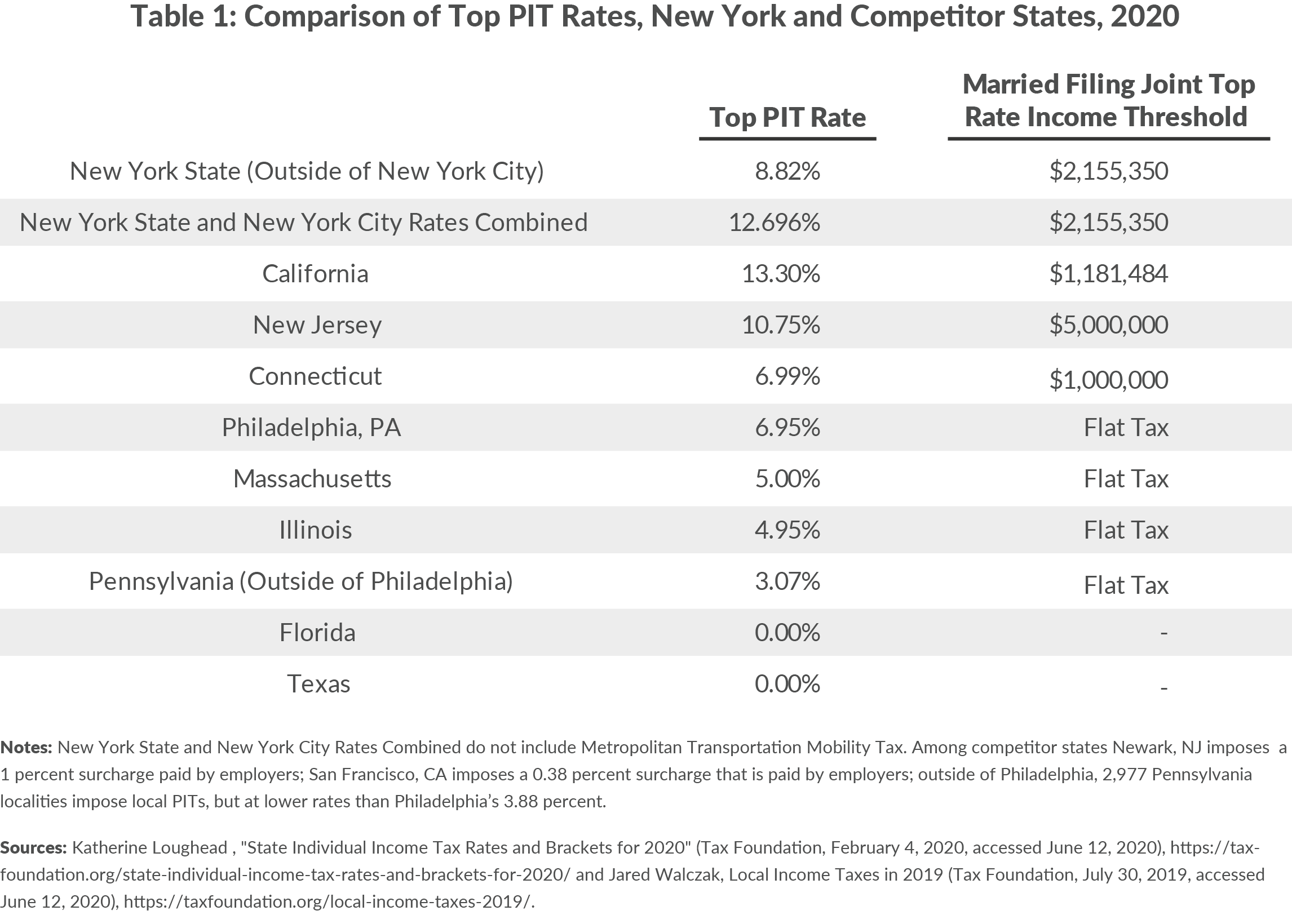
New York State Income Tax
New York state income tax is a significant source of revenue for the state. It applies to both residents and non-residents who earn income within the state. The tax rates vary depending on your income level, with higher earners paying a larger percentage of their income.
Income Tax Rates
As of 2023, the New York state income tax rates are as follows:
- 4% for income up to $8,500
- 4.5% for income between $8,501 and $11,700
- 5.25% for income between $11,701 and $13,900
- 5.97% for income between $13,901 and $21,400
- 6.09% for income between $21,401 and $80,650
- 6.33% for income over $80,650
These rates are subject to change, so it's essential to stay updated with the latest regulations.
Read also:King Von Death The Untold Story Of A Rising Star Cut Short
Sales Tax in New York
Sales tax in New York is another critical component of the state's tax system. It is applied to most retail purchases, with rates varying across counties and municipalities.
Sales Tax Rates
The statewide sales tax rate is 4%, but local jurisdictions can add additional taxes, resulting in rates ranging from 4% to over 9%. For example:
- New York City: 4.545% local tax + 4% state tax = 8.875% total
- Westchester County: 4% local tax + 4% state tax = 8% total
Some items, such as clothing and footwear under $110, are exempt from sales tax in certain counties.
Property Taxes in New York
Property taxes in New York are assessed at the local level and are a major source of funding for schools and local governments. These taxes are based on the assessed value of your property.
Assessment Process
Local assessors determine the market value of your property and then apply an assessment rate, which is typically around 100% of market value. Property taxes are calculated by multiplying the assessed value by the tax rate.
For example, if your home is assessed at $300,000 and the tax rate is 1%, your annual property tax would be $3,000.
Business Taxes in New York
New York imposes several types of taxes on businesses, including corporate income tax, franchise tax, and sales tax. These taxes are designed to ensure that businesses contribute to the state's revenue.
Corporate Income Tax
The corporate income tax rate in New York is 6.5%, with additional surcharges for corporations with higher profits. Small businesses may qualify for reduced rates or exemptions.
Additionally, businesses must pay a franchise tax, which is based on their net worth or income, whichever is greater.
Estate and Inheritance Taxes
New York imposes estate taxes on the estates of deceased individuals, with exemptions and rates that vary depending on the size of the estate. Inheritance taxes are not levied in New York, but beneficiaries may still owe federal estate taxes.
Estate Tax Exemptions
As of 2023, the New York estate tax exemption is $6,285,000. Estates valued below this amount are exempt from state estate taxes. However, estates exceeding this threshold are taxed at rates up to 16%.
Tax Exemptions and Credits
New York offers various tax exemptions and credits to help taxpayers reduce their tax burden. These include:
- Homestead exemptions for property taxes
- Child tax credits
- Earned income tax credit for low-income individuals
- Education credits for tuition and related expenses
Taking advantage of these exemptions and credits can significantly lower your tax liability.
Filing Your New York Tax Return
Filing your New York tax return is a crucial step in fulfilling your tax obligations. The deadline for filing is typically April 15th, although extensions can be requested if necessary.
Steps for Filing
To file your New York tax return:
- Gather all necessary documents, including W-2 forms, 1099s, and receipts for deductions.
- Use the appropriate tax forms, such as IT-201 for personal income tax.
- Submit your return electronically or by mail, ensuring all information is accurate and complete.
Electronic filing is often faster and more secure, and it allows you to receive refunds more quickly.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with New York tax laws can result in significant penalties, including fines and interest on unpaid taxes. It's essential to file your return on time and pay any taxes owed to avoid these consequences.
Common Penalties
Penalties for non-compliance may include:
- Failure-to-file penalty: 5% of unpaid taxes per month, up to 25%.
- Failure-to-pay penalty: 0.5% of unpaid taxes per month.
- Interest charges on unpaid taxes.
Consulting a tax professional can help you avoid these penalties and ensure compliance with all regulations.
Useful Resources for Taxpayers
Several resources are available to assist taxpayers in understanding and managing their New York tax obligations:
- New York State Department of Taxation and Finance website
- IRS website for federal tax information
- Local tax offices for personalized assistance
These resources provide valuable information on tax laws, forms, and filing procedures, helping you stay informed and compliant.
Conclusion
New York taxes play a vital role in funding public services and infrastructure, but they can be complex and challenging to navigate. By understanding the different types of taxes, their rates, and available exemptions, you can better manage your financial obligations and optimize your tax planning.
We encourage you to explore the resources mentioned in this guide and consult with a tax professional if needed. Your feedback and questions are valuable, so please leave a comment or share this article with others who may find it useful. Together, let's ensure a better understanding of New York taxes and their impact on our lives.