Understanding New York State taxes is crucial for both individuals and businesses operating in the Empire State. Whether you're a resident, a business owner, or planning to relocate, having a clear grasp of the tax system can help you make informed financial decisions. This guide provides a detailed overview of the key aspects of New York State taxes, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, and other relevant taxes that may affect you.
New York State is known for its robust economy and vibrant communities, but it also has one of the most complex tax systems in the United States. Navigating this system can be challenging, especially for newcomers or those unfamiliar with state-specific regulations. This article aims to simplify the process by breaking down the various components of New York State taxes.
By the end of this guide, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how New York State taxes work, the rates you can expect, and strategies to optimize your tax liabilities. Let's dive in and explore the intricacies of New York's tax landscape.
Read also:Amber Heard And Jason Momoa Together Exploring Their Connection
Table of Contents
- New York State Income Tax
- Sales Tax in New York State
- Property Tax Overview
- Business Taxes in New York
- Estate and Inheritance Taxes
- Tax Deductions and Credits
- Filing Your New York State Taxes
- Penalties for Late or Incorrect Filing
- Useful Resources for Taxpayers
- Conclusion and Next Steps
New York State Income Tax
New York State income tax is a significant component of the state's tax structure. It applies to all residents, part-year residents, and non-residents who earn income within the state. The tax rates are progressive, meaning that higher income levels are subject to higher tax rates.
2023 Income Tax Rates
For the 2023 tax year, New York State income tax rates range from 4% to 10.90%. The rates are structured as follows:
- 4% on the first $8,700 of taxable income
- 4.5% on income between $8,701 and $11,700
- 5.25% on income between $11,701 and $23,400
- 5.97% on income between $23,401 and $1,088,650
- 6.33% on income between $1,088,651 and $5,078,125
- 10.90% on income above $5,078,125
These rates are subject to change, so it's essential to stay updated with the latest regulations.
Sales Tax in New York State
Sales tax in New York State is another critical aspect of the tax system. The state imposes a general sales tax rate of 4%, with additional local taxes that can increase the total rate to as much as 9.875% in some areas.
How Sales Tax Works
Sales tax applies to most goods and services purchased within the state. Certain items, such as groceries and prescription medications, are exempt from sales tax. However, non-prescription medications and prepared foods are generally subject to taxation.
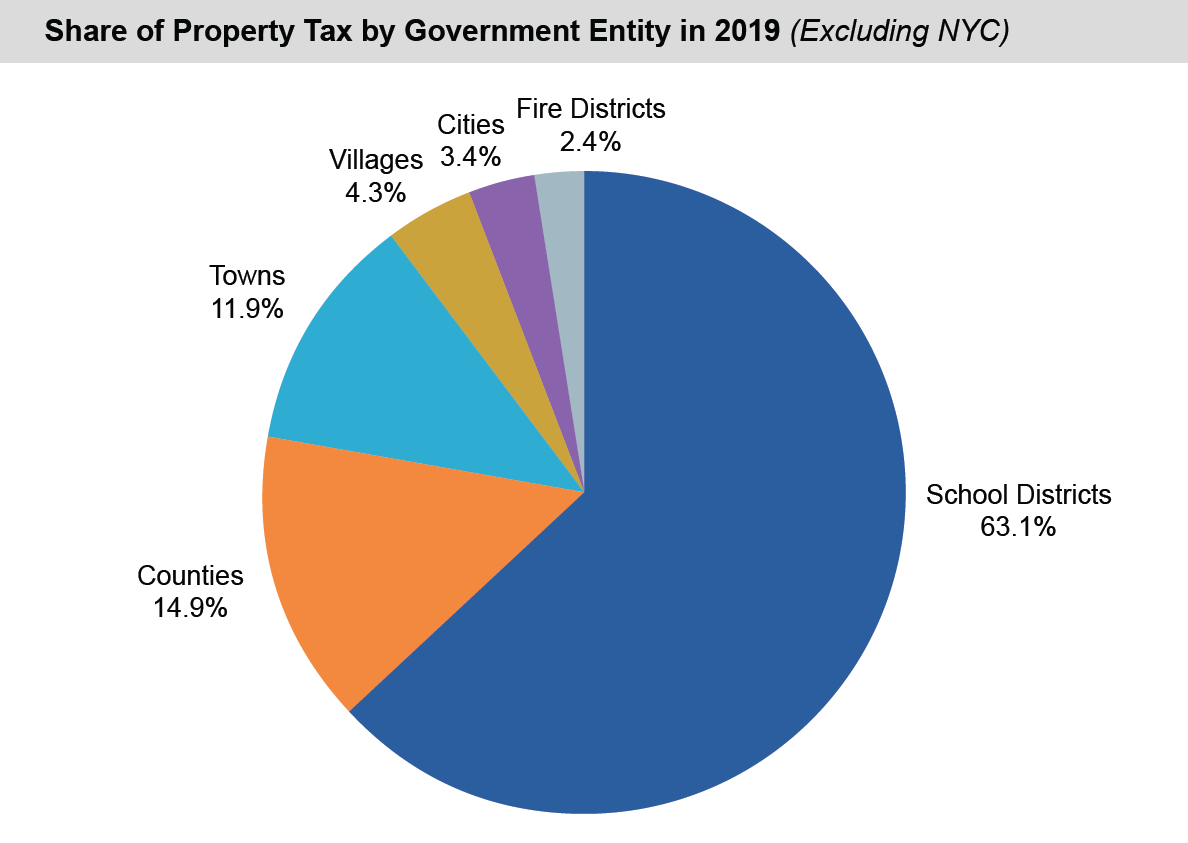
Property Tax Overview
Property taxes in New York State are levied by local governments and are a major source of revenue for schools, municipalities, and other public services. The tax rates vary significantly across different regions, depending on local budgets and property values.
Read also:Vertical Ridges On Nails A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Vitamin Deficiency And Its Impact
Factors Affecting Property Tax Rates
Several factors influence property tax rates in New York, including:
- Assessed value of the property
- Local government budget requirements
- Exemptions and abatements available to homeowners
Homeowners can apply for various exemptions, such as the School Tax Relief (STAR) program, to reduce their property tax burden.
Business Taxes in New York
Businesses operating in New York State are subject to various taxes, including corporate income tax, franchise tax, and sales tax. The specific taxes a business must pay depend on its structure, industry, and location.
Corporate Income Tax Rates
As of 2023, the corporate income tax rate in New York State is 6.5%. However, additional surcharges may apply to corporations with higher income levels. It's important for businesses to consult with tax professionals to ensure compliance and optimize their tax strategies.
Estate and Inheritance Taxes
New York State imposes an estate tax on the transfer of assets upon the death of an individual. The tax is calculated based on the value of the estate and is subject to certain exemptions and exclusions.
2023 Estate Tax Exemption
For the 2023 tax year, the New York State estate tax exemption is set at $6,375,000. Estates valued below this threshold are generally not subject to taxation. However, larger estates may face significant tax liabilities.
Tax Deductions and Credits
New York State offers several deductions and credits to help taxpayers reduce their tax burden. These include:
Key Deductions
- Personal exemptions
- Child care expenses
- Student loan interest
Popular Credits
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit
- Property tax credit
Taking advantage of these deductions and credits can result in substantial savings for taxpayers.
Filing Your New York State Taxes
Filing your New York State taxes can be done electronically or by mail. The deadline for filing is typically April 15th, although extensions can be requested if necessary.
Steps to File Electronically
Electronic filing is the preferred method for most taxpayers due to its convenience and speed. Here are the steps to file your taxes electronically:
- Gather all necessary documents, including W-2s, 1099s, and receipts for deductions.
- Choose a certified tax preparation software or service.
- Enter your information accurately and review for errors.
- Submit your return and pay any owed taxes or request a refund.
Penalties for Late or Incorrect Filing
Failing to file your New York State taxes on time or making errors in your return can result in penalties and interest charges. It's crucial to adhere to the filing deadlines and ensure the accuracy of your submission.
Common Penalties
- Failure-to-file penalty: 5% of unpaid taxes per month, up to 25%.
- Failure-to-pay penalty: 0.5% of unpaid taxes per month.
- Interest charges on unpaid taxes.
Avoiding these penalties requires careful planning and attention to detail when preparing your tax return.
Useful Resources for Taxpayers
Several resources are available to assist taxpayers in understanding and complying with New York State tax regulations. These include:
- New York State Department of Taxation and Finance website
- IRS publications and guides
- Tax preparation software and services
Utilizing these resources can help ensure a smooth and stress-free tax filing process.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, New York State taxes encompass a wide range of categories, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, and business taxes. Understanding these components and staying informed about the latest regulations is essential for managing your financial responsibilities effectively.
We encourage you to take the following actions:
- Review your tax situation and identify potential deductions and credits.
- Consult with a tax professional if you have complex financial needs.
- Stay updated with the latest tax laws and regulations.
Feel free to share this article with others who may benefit from it, and don't hesitate to leave a comment or question below. For more information on New York State taxes, explore our other articles and resources.